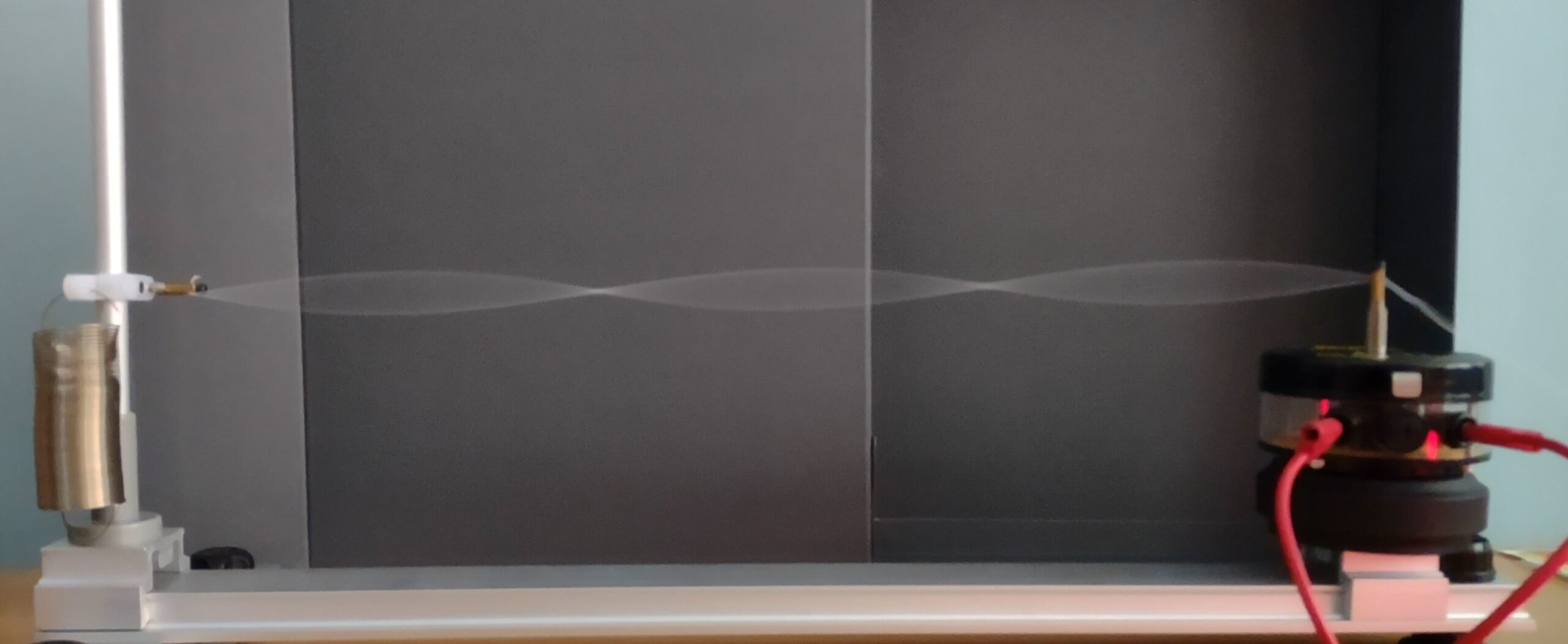
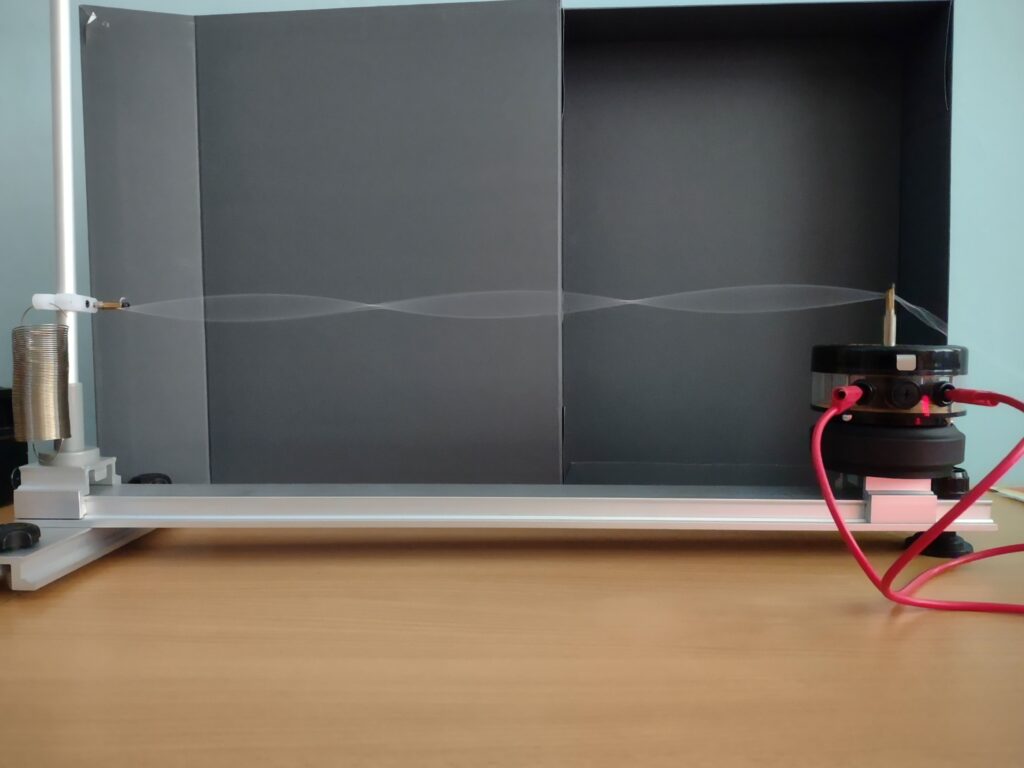
Static waves
A standing wave is called the result of the contribution of two waves of the same frequency and the same width that are propagated in the same medium with opposite directions.
When two or more waves are propagated in an elastic medium, we use the principle of superposition, according to which: When two or more waves are propagated in an elastic medium, the displacement of a point of the medium is equal to the sum of the displacements due to the individual waves.
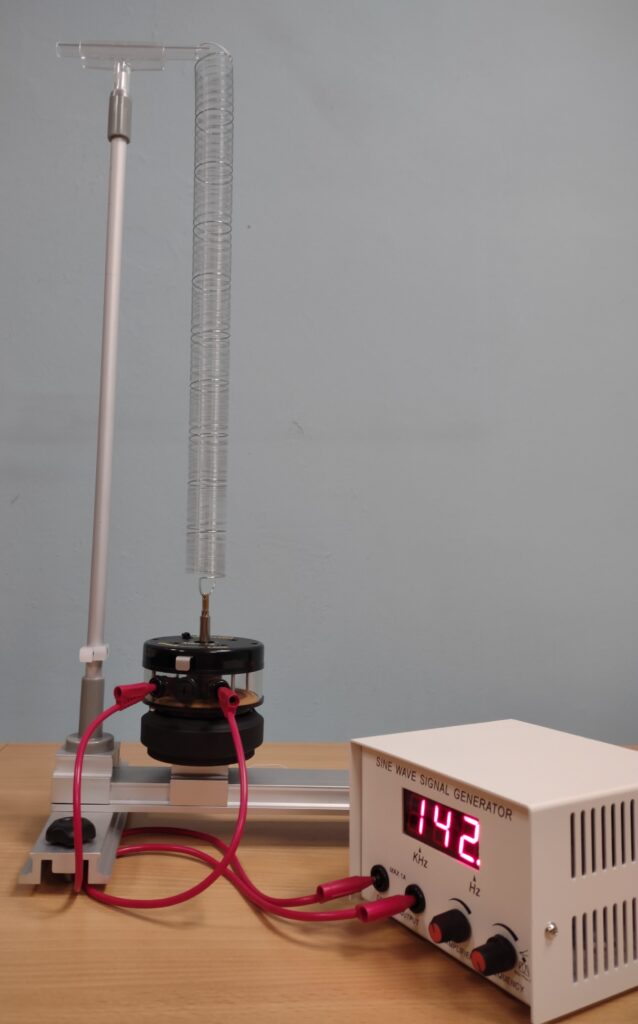

Experiment materials:
- Frequency generator with adjustable intensity and frequency control
- Electromechanical oscillator (1Hz to 4.00kHz step 0.01kHz)
- Support base with guide (for moving the oscillator)
- Ruler for studying standing wave lengths
- String for studying standing wave nodes
Procedure:
We assemble the arrangement as shown in the image. We adjust the frequencies so that we can observe the standing waves.
Explanation:
The standing wave that we observe is the result of the contribution of the wave produced by the electromechanical oscillator and that which is reflected when it reaches the end of the string or ruler. The nodes and troughs are shown in the string standing wave and the compressions and rarefactions in the wavelength.

